Nutritionists Love Persimmons Because Of These 3 Health Benefits
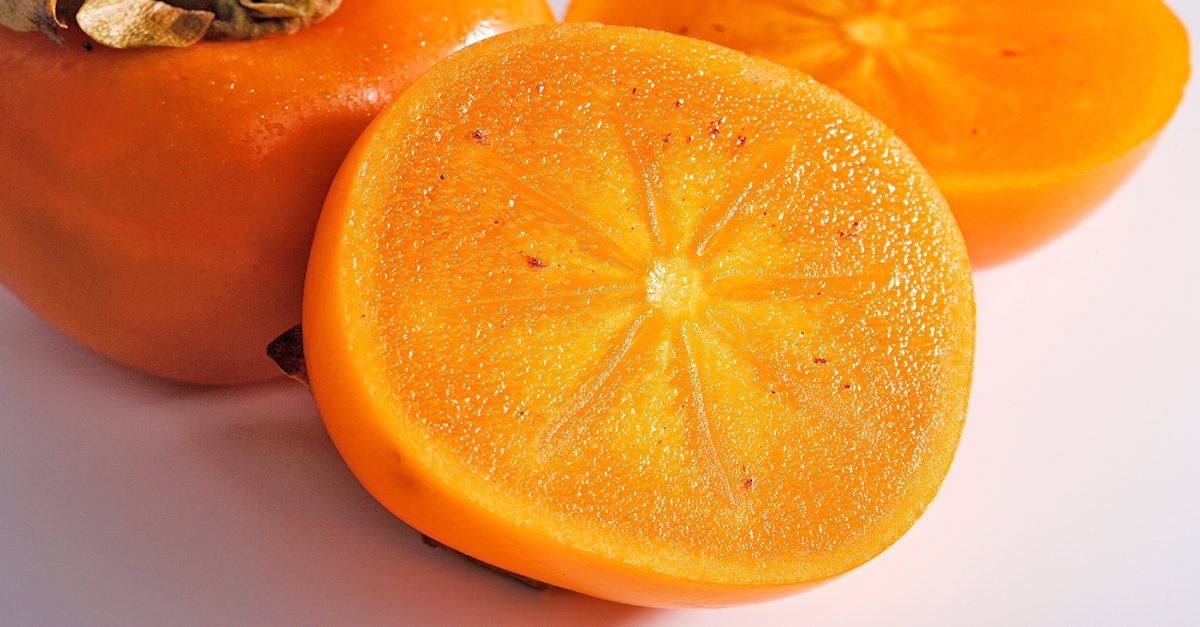
Persimmon trees originated from China where they were cultivated for thousands of years for their sweet fruit and attractive wood. Their fruits, which are orange colored are famous for their sweet and honeylike flavor however not many are aware of how nutritious they are. Keep reading to get in the know.
;Resize,width=742;)

There are over a hundred types of persimmons but the two most popular are the Hachiya and Fuyu varieties. Hachiya persimmons are high in plant chemicals called tannins and they give the unripe fruit a dry and bitter taste.
That’s why the hachiya persimmon has to be ripe before it can be consumed. In contrast, fuyu persimmons can be enjoyed before they are fully ripe. This is not to say they don’t contain tannins; they do, however the quantity is considerable less enough for them to be classified as astringent.
Persimmons can be enjoyed fresh, dried and cooked. They are commonly used globally in jellies, drinks, pies, curries, and puddings. Below are some health benefits associated with persimmons.
1. They are nutrient dense

Persimmons may be small but they are packed with a healthy amount of nutrients. They are also a great source of thiamin (B1), riboflavin (B2), folate, magnesium, and phosphorus.
One persimmon contains:
- Calories: 118
- Carbs: 31 grams
- Protein: 1 gram
- Fat: 0.3 grams
- Fiber: 6 grams
- Vitamin A: 55% of the RDI
- Vitamin C: 22% of the RDI
- Vitamin E: 6% of the RDI
- Vitamin K: 5% of the RDI
- Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine): 8% of the RDI
- Potassium: 8% of the RDI
- Copper: 9% of the RDI
- Manganese: 30% of the RDI
2. They contain great antioxidants

Persimmons have antioxidant qualities that can prevent or slow down cell damage by counteracting oxidative stress triggered by free radicals. Left unchecked, oxidative stress can cause chronic diseases but foods like persimmon are great for fighting it off.
3. They are good for heart health

Persimmons have a powerful combination of nutrients that make them perfect for boosting heart health. They contain flavonoid antioxidants, including quercetin and kaempferol. They also contain tannic and gallic acid, both of which are great at lowering high blood pressure.
How to incorporate persimmons into your diet
Here are some of our favorite ways to use persimmons:
- Use them to prepare a salad
- Use them to top your yogurt or oatmeal
- They can be roasted in the oven and garnished with honey for a healthy dessert
- They can be used in the making of muffins, cakes, or breads.
- They make great appetizers if you broil them and serve with baked brie
- They can be baked with chicken or other meat
- They make great ingredients for a smoothie
- They can be used to make natural fruits strips.
Enjoy!
;Resize,width=767;)
;Resize,width=712;)
;Resize,width=712;)
;Resize,width=712;)
